Acne vulgaris is the most common skin disease in countries. It usually begins during puberty, at the same time as hormonal changes, and can persist into late adulthood. Around 80 to 90% of young people are affected to some degree by impurities, and between 20 to 30% of these people will seek medical support. The number of adults, especially women, who experience acne later in life is also increasing.
What is acne?
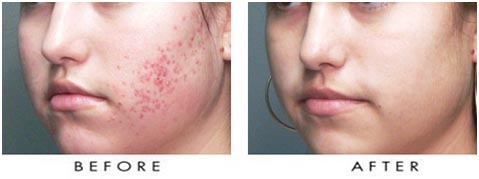
In acne the skin is oily and open and closed (black head and white head) appear on the face and often on the neck, shoulders, chest and back as well. In moderate and severe acne, the skin becomes red and inflamed papules and pustules appear. Acne can be emotionally distressing, untimely persistent, and can lead to long-term post- inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) and / or scar retraction.
Main causes and triggers of acne
Hormones are thought to play a role in making acne more common in teens (although acne can affect people of all ages). The increase in androgens in both boys and girls at puberty causes the sebaceous glands to produce more sebum than is needed by the skin.
Apart from the amount of circulating hormones, the increased sensitivity of the sebaceous glands is also important for the development of acne.
Most cases of acne disappear spontaneously after puberty. However, effective treatment is necessary to prevent the formation of persistent scars.
Since the sebaceous glands are especially sensitive to hormones, adult acne can appear in women with hormone-related processes, such as polycystic ovary syndrome. Psychological stress can also be a trigger for adult female acne.
Bacteria In people with acne-prone skin, excess sebum production creates an ideal environment in which normally harmless acne bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes) can multiply. This triggers inflammation and the formation of red or pus-filled spots.
Contrary to what certain myths would have you believe, this is not because people with acne are unhygienic. On the contrary, excessive cleaning with harsh cleansers is actually more likely to irritate the skin.
The existence of genes that affect people’s risk of acne is also considered. Thus, if both parents suffer from acne, there is a greater chance that their child will also have this process.
Similarly, if one or both parents have adult acne, their offspring carry a greater chance of getting adult acne as well.
Medication.
Certain medications, such as steroids and lithium, are known to trigger acne in some people.
Main contributing factors of acne
While they are not a cause of acne, some elements are known to aggravate symptoms:
- Diet too rich in certain carbohydrates (large amounts of sugar and white flour)
- Excessive consumption of cow’s milk and dairy products (except cheese)
- Smoking cigarettes
- Makeup that clogs the pores
- Comedogenic skin care products
What medical treatments are available?
Effective medications that can be used to treat acne include the following:
- Topical retinoids
- Benzoyl peroxide
- Topical antimicrobials
- Azelaic acid
- Oral antibiotics
- Oral contraceptives
These medications are used alone or in combination, and the dermatologist will prescribe the appropriate medication based on the severity of the symptoms.
The medical treatment of acne follows a strict international standard to ensure that dermatologists and physicians are consistent in their treatment. This science-based standard * provides practicing physicians with information on which treatments or combination of treatments to use, based on the severity of acne and individual symptoms. It offers alternatives to take into account different skin types, as well as options, if applicable, for female patients.
Since certain oral prescription acne medications should not be used during pregnancy, especially during the first trimester, dermatologists and doctors may suggest alternatives.
It is worth noting that acne treatment, medicinal or non-medicinal, takes time to take effect.
Although the general rule of thumb is 4-8 weeks, it may take as long as three months; Also, symptoms may get worse before they get better. Since it is easy for patients to get discouraged and drop out, it is important to persevere and stick with the guidelines, even if there is no immediate change for the better.