Vitiligo Treatment in Punjabi Bagh, Delhi by Dr. Vijay Singhal, Dermatologist at Zenith Skin & Dental Clinic
Vitiligo, a condition that affects the skin’s pigmentation, can be emotionally challenging for many. While it doesn’t pose any physical threat, its visual impact on the skin can cause social and psychological stress. Finding the right vitiligo treatment in Punjabi Bagh, Delhi is crucial, and for those living in this area, Dr. Vijay Singhal, a renowned dermatologist at Zenith Skin & Dental Clinic, offers effective solutions.
What is Vitiligo?
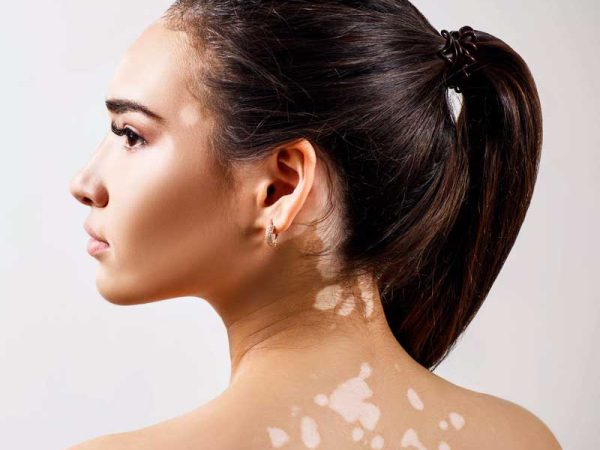
Vitiligo is a skin disorder characterized by patches of skin losing their pigment. These patches occur when melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing skin pigment, are destroyed. The loss of pigmentation can appear on various parts of the body, including the face, arms, hands, and feet.

A common misconception is that vitiligo only affects people with darker skin tones. In reality, it can affect anyone, regardless of their skin color.
Causes of Vitiligo
The exact cause of vitiligo isn’t entirely understood. However, it is widely believed to be an autoimmune disorder. This means the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its melanocytes, leading to the loss of pigment in the skin.
Factors that may contribute to vitiligo include:
- Genetics: Vitiligo often runs in families.
- Autoimmune conditions: Individuals with other autoimmune diseases are at a higher risk.
- Environmental factors: Stress, exposure to harmful chemicals, and sunburns may trigger vitiligo.
Types of Vitiligo
There are two main types of vitiligo:
- Segmental Vitiligo: Typically affects only one part of the body and tends to progress for a year or two before stopping.
- Non-Segmental Vitiligo: More common, affecting both sides of the body symmetrically. It often starts in areas like the hands, wrists, or face and may spread over time.
Symptoms of Vitiligo
The most prominent symptom of vitiligo is the development of white patches on the skin. These patches are more visible in areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and hands. Other symptoms may include:
- Premature graying of hair.
- Loss of color inside the mouth or nose.
- Changes in eye color.
Psychological Impact of Vitiligo
Living with vitiligo can be emotionally overwhelming. Many individuals feel self-conscious about their appearance, leading to anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal. Vitiligo isn’t just a skin condition; it can deeply affect a person’s mental well-being.
Just like a chipped vase may still hold flowers, people with vitiligo are just as capable of leading fulfilling lives.
Treatment Options for Vitiligo
When it comes to treating vitiligo, a one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work. Different treatments are effective for different people, depending on the type and severity of vitiligo. At Zenith Skin & Dental Clinic, Dr. Vijay Singhal offers a variety of vitiligo treatment in Punjabi Bagh, Delhi, including:
- Topical corticosteroids: These creams help reduce inflammation and may restore pigment.
- Light therapy (PUVA): Involves exposure to UV light to stimulate pigment production.
- Surgical options: In certain cases, skin grafts or melanocyte transplants are viable options.
- Depigmentation therapy: For those with widespread vitiligo, depigmenting the unaffected areas may offer a more uniform skin tone.
Why Choose Dr. Vijay Singhal?
Dr. Vijay Singhal is a highly respected dermatologist with years of experience in treating vitiligo. His compassionate approach, combined with his deep understanding of the condition, makes him one of the top choices for patients seeking vitiligo treatment in Delhi.
Dr. Singhal’s philosophy revolves around personalized care. He tailors each treatment plan to the patient’s needs, ensuring optimal results.
Vitiligo Treatment in Punjabi Bagh, Delhi at Zenith Skin & Dental Clinic
At Zenith Skin & Dental Clinic, you can expect state-of-the-art facilities, a friendly environment, and a dedicated team of professionals. Dr. Vijay Singhal uses the latest technology and medical advancements to offer the best vitiligo treatment in Punjabi Bagh, Delhi.
What to Expect During Treatment
When you visit Zenith Skin & Dental Clinic, your journey begins with a detailed consultation. Dr. Vijay Singhal will assess your condition, understand your concerns, and discuss the available treatment options. Whether you require topical treatments, light therapy, or surgery, Dr. Singhal will ensure you are comfortable throughout the process.
Home Care Tips for Vitiligo
Managing vitiligo doesn’t stop at the clinic. Here are a few home care tips to help maintain your skin’s health:
- Sun protection: Always use sunscreen to protect depigmented areas from UV damage.
- Moisturize regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated can help improve its overall appearance.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants can support skin health.
Success Stories of Vitiligo Treatment
Many patients at Zenith Skin & Dental Clinic have experienced significant improvement in their vitiligo after treatment. These success stories are a testament to Dr. Vijay Singhal’s expertise and dedication.
Is Vitiligo Curable?
While there isn’t a definitive cure for vitiligo, modern treatments can help restore pigment and stop its progression. With timely intervention and the right care, many individuals can achieve remarkable results.
How to Book a Consultation
Booking a consultation with Dr. Vijay Singhal is easy. You can either visit the Zenith Skin & Dental Clinic in Punjabi Bagh or book an appointment online. Early intervention can make a huge difference in the success of vitiligo treatment, so don’t hesitate to take the first step.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can vitiligo spread to other parts of the body?
Yes, vitiligo can spread to other areas of the body, though its progression varies from person to person.
2. Is vitiligo contagious?
No, vitiligo is not contagious. It cannot be passed from one person to another through contact.
3. How long does vitiligo treatment take?
The duration of vitiligo treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the treatment approach. Some treatments show results within months, while others may take longer.
4. Can vitiligo return after treatment?
There is a chance that vitiligo can return, but ongoing treatment and follow-up care can help manage the condition.
5. Will my skin return to its original color after treatment?
While some treatments can restore pigment, complete recovery is not always guaranteed. The extent of improvement varies from patient to patient.
In conclusion, Dr. Vijay Singhal at Zenith Skin & Dental Clinic offers hope and effective treatment options for those dealing with vitiligo in Punjabi Bagh and Delhi. If you’re looking for professional care and compassionate support, Dr. Singhal and his team are ready to help you on your journey to healthier skin.